Consumables-from food to pharmaceuticals and supplements are becoming increasingly vulnerable to various modes of counterfeiting due to the growing complexity of their supply chain. Mislabeling, re-branding, and false advertising are prevalent in this sector.
Trust is becoming an increasingly important factor in the life-cycle of consumables, from medicines to dietary supplements and diverse food products. This is primarily due to the complex and globally distributed nature of their supply chain, which often involves many untrusted parties at different stages– from manufacturing to distribution.
Existing physical authentication techniques fail to adequately verify integrity of these products and protect the end-users.
Existing solutions, such as regulations for appropriate product labeling and package-level tagging, suffer from major deficiencies. While it is mandatory for manufacturers to provide a complete breakdown of the ingredients, there are few techniques available for authenticating the quality of these ingredients. Moreover, the globally distributed nature of the supply chain leads to the lack of communication and assignment of responsibility between involved parties. This provides opportunities for counterfeiters to enter into a supply chain, giving an opportunity to various types of fraud.
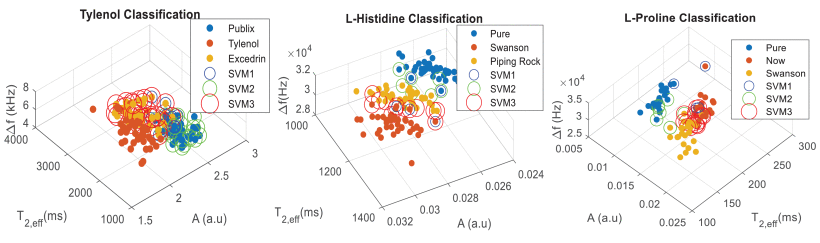
Nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) is quantitative, non-invasive, low-cost, and amenable for miniaturization (to hand-held form factors). The method is sensitive to small variations in the solid-state chemical structure of a sample, which changes the NQR signal properties.
These attributes can be unique for various manufacturers, enabling their use as manufacturer-specific watermarks. However, NQR spectroscopy only works reliably (i.e., provides good sensitivity) on compounds that contain certain nuclear isotopes. We take advantage of the intrinsic properties of NQR-sensitive isotopes to use them as extrinsic tags in NQR-insensitive products. The NQR spectra of these extrinsic tags act as unique watermarks that can be analyzed using machine learning methods to authenticate any consumable with high confidence.